Methodologies and "How To"
IDEAS-Classic
Problem Statement
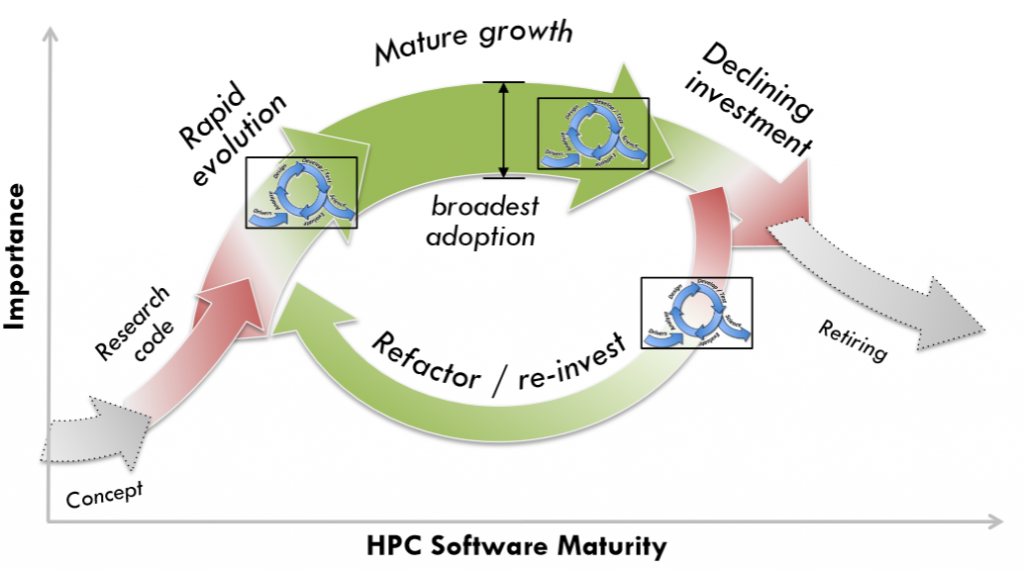
Software productivity (the effort, time, and cost for software development, maintenance, and support) is one critical aspect of scientific productivity. Therefore, although general and actionable productivity metrics are very difficult to define, an overarching focus on productivity is essential to making clear decisions in this time of highly disruptive architectural changes. In this project we are focusing on improving productivity by defining and taking steps toward a new scientific software ecosystem that emphasizes the use and development of high-quality tools, adaptation and adoption of modern software engineering methodologies, and the development and use of high-quality software components in the composition of next-generation applications.
Scoping
- Identify useful Software Engineering Methodologies relevant to extreme-scale scientific computing
- Test these methodologies in real-world use cases that involve BER science applications throughout their lifecycles
- Document and publish useful software productivity methodologies as “How-To’s” for use by the broader HPC scientific computing community
Approaches
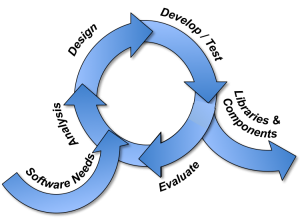
- Training, documentation, and other aids to application teams to help them be their most productive
- Software lifecycle models and instruction on agile/lean methodologies that promote rapid development of high-quality applications, leveraging the new software ecosystems and contributing to them
- Harvesting from use case and toolkit experiences within existing ASCR tool sets
- Documenting the IDEAS team’s best practices, with HPC context
Connections with other IDEAS areas
- The Basics to establish software engineering best practices in the Science Application areas
- Extreme-scale considerations to prepare for science use cases at scale
- Software productivity improvements that connect science use cases, HPC, and lifecycle considerations